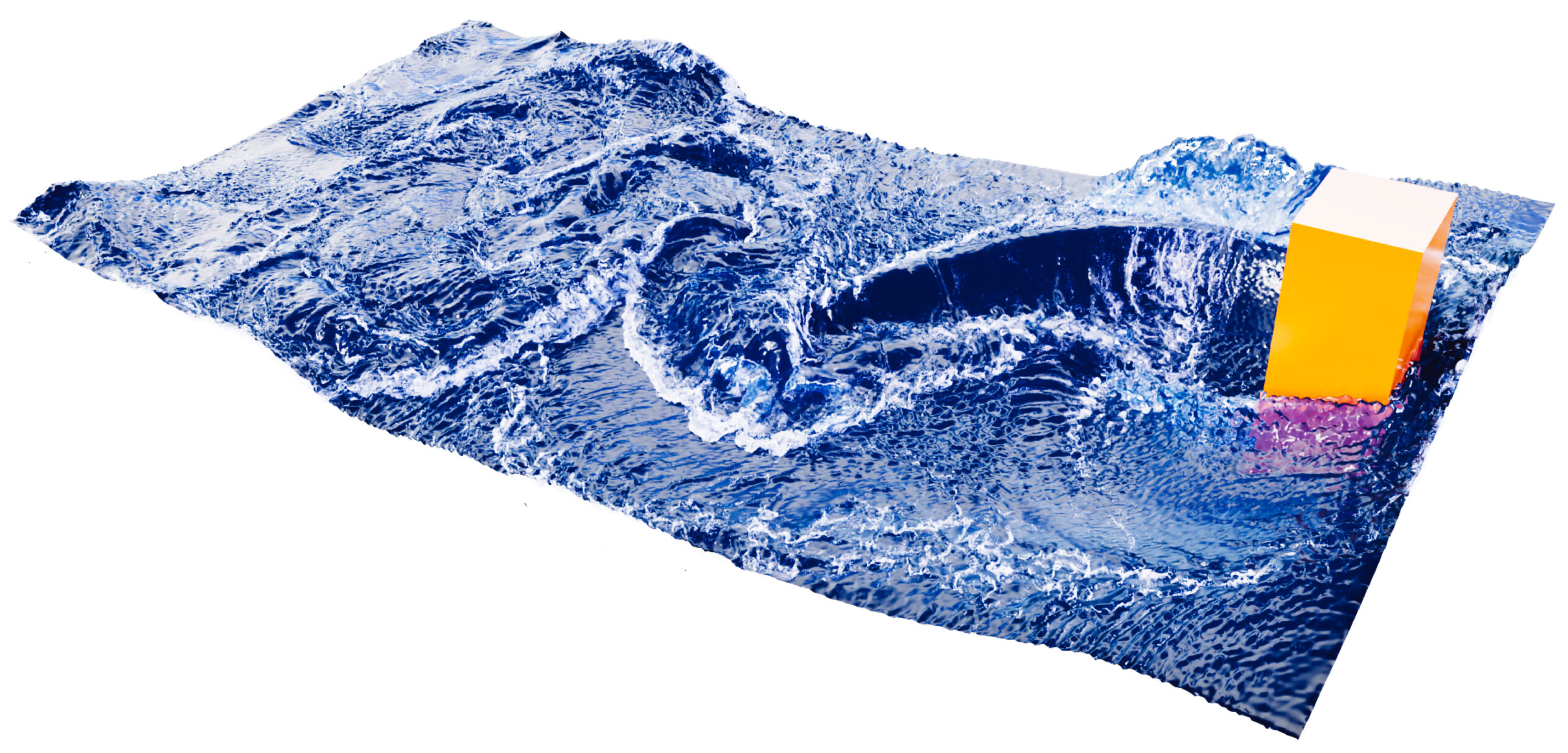
Water flow generated by pillar in sinusoidal motion (from PhD research Yous van Halder)
Scientific Computing (SC) enables the simulation of phenomena, processes and systems that cannot be studied by real experiments for technical, financial, safety or ethical reasons. SC also allows for automatic design and optimization, through inverse computations. Many disciplines in science and engineering have their own computational branches now. With continuing growth in speed, memory and cost-effectiveness of computers and similar improvements in numerical mathematics, the future benefits of SC are enormous.
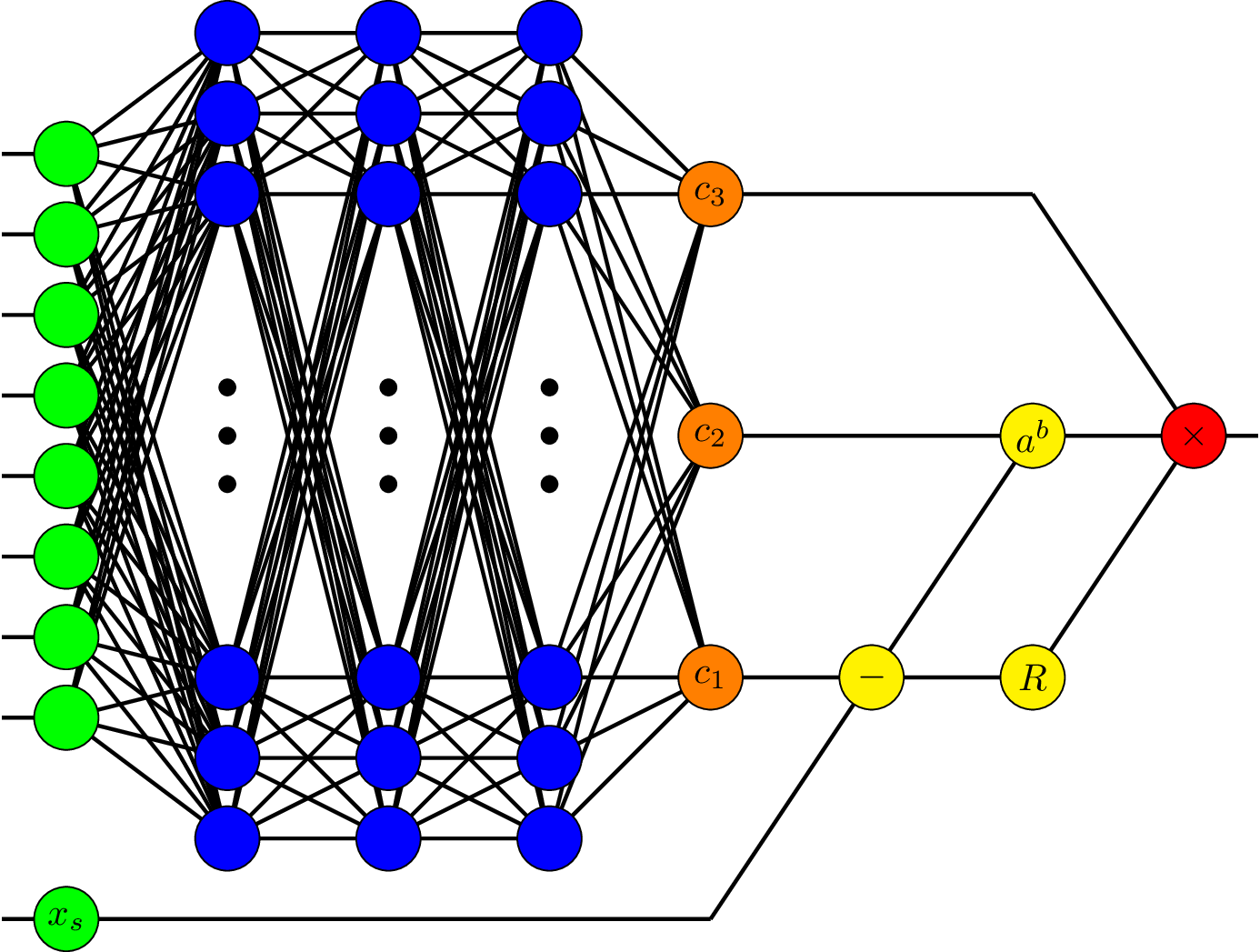
Within CASA’s SC group, we propose, analyze, develop and implement new numerical mathematics methods, particularly structure-preserving discretization methods for partial differential equations and numerical linear algebra methods for linear systems of equations. We carry over these methods to Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), for application to particularly fluid-structure-interaction and energy-conversion problems.

Air vortices generated by impulsively started wind-turbine model blade (from PhD research René Beltman)